Understanding 4-Way Pneumatic Valves: Choosing the Right Valve for Your Application
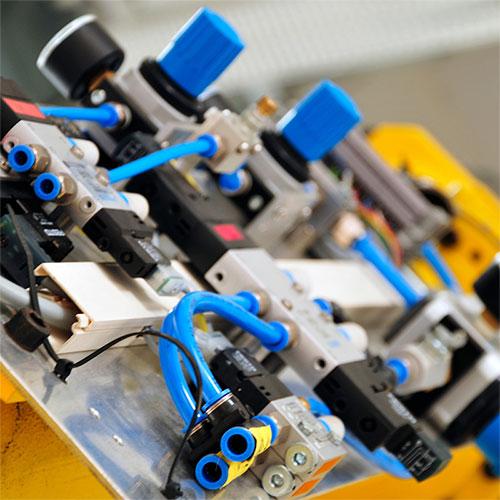 When your application demands precise control of pneumatic actuators, choosing the correct valve is crucial. Even slight inefficiencies or inappropriate valve selections can reduce system performance, operational delays, and increased maintenance costs. Navigating the options can be overwhelming, especially with something as nuanced as 4-way pneumatic valves, which are pivotal in accurately directing airflow for actuator movements.
When your application demands precise control of pneumatic actuators, choosing the correct valve is crucial. Even slight inefficiencies or inappropriate valve selections can reduce system performance, operational delays, and increased maintenance costs. Navigating the options can be overwhelming, especially with something as nuanced as 4-way pneumatic valves, which are pivotal in accurately directing airflow for actuator movements.
A clear understanding of 4-way valve types and their specific uses ensures your pneumatic system operates reliably, efficiently, and with the precision your processes demand. By matching valve features to your exact application, you eliminate guesswork and maximize productivity.
Four-Way Directional Pneumatic Valves: Comprehensive Technical Overview
Four-way directional valves, also commonly referred to as "4-way valves," serve a fundamental role within pneumatic systems due to their ability to manage airflow to and from actuators or pneumatic cylinders. They provide precise control of actuator extension and retraction by directing compressed air to opposite sides of an actuator, allowing accurate and reliable reversal of movement.
Key Functional Principles
A standard four-way directional valve has four distinct ports, each serving a specific and clearly defined role.
- Port 1 (Supply Port): Receives compressed air from the system's primary air supply line.
- Ports 2 and 4 (Actuator Ports): These ports connect directly to either side of a double-acting pneumatic cylinder or rotary actuator, facilitating controlled and reversible movement.
- Port 3 (Exhaust Port): This port allows air to flow from the actuator's opposite side to the vent, allowing smooth cycling of actuator movements.
The core functionality is straightforward yet critical: when the valve shifts position, airflow direction changes, actuating devices to perform precise movements. Depending on the actuator connected, this might mean extending and retracting a pneumatic cylinder or switching rotational directions in rotary actuators.
Valve Configurations and Positions
Four-way valves typically come in two main position-based configurations: two-position and three-position. Each configuration has specific use cases and distinct operational characteristics.
- Two-Position Four-Way Valves: These valves switch between two discrete states. In one position, compressed air flows into one actuator port while the other is exhausted. When the valve shifts, the airflow direction reverses.
- Typical Application: Ideal for operations requiring simple extend-and-retract movements, such as industrial clamping, pressing, or basic linear actuator cycling.
- Three-Position Four-Way Valves: These valves feature a neutral, or "center," position in addition to the two operational states. This center position significantly impacts actuator behavior when the valve is inactive and is available in several variations.
- All Ports Open (Center Exhaust): Cylinder ports are vented to the atmosphere, allowing free movement. This is useful in systems requiring manual repositioning or emergency venting.
- All Ports Closed (Center Closed): Locks the actuator firmly in place, preventing unintended motion. Beneficial for holding precise positions under load.
- Pressure Center: Both actuator ports maintain pressure, holding actuators steadily with balanced pneumatic pressure. This configuration is optimal for applications where maintaining constant pressure in both cylinder chambers is critical to operation.
Material Construction and Durability
Robust construction is critical for industrial applications. Ellis Kuhnke Controls' four-way valves are constructed using precision die-cast aluminum or zinc bodies, ensuring reliable, leak-free operation even under demanding conditions. Porting is available in standard NPT (National Pipe Thread) and Metric thread configurations to accommodate international standards, ensuring compatibility and ease of integration into global pneumatic systems.
Specific Industry Applications
Four-way directional valves are indispensable in various industrial automation systems due to their adaptability and precision control.
- Automated Assembly Lines: Precise and repetitive actuator movement is critical to assembly operations where timing and positioning accuracy are paramount.
- Robotics: Requires exact directional control for manipulating arms and grippers, essential for precision tasks in manufacturing or packaging.
- Material Handling: Enables automated lifting, positioning, and controlled movements in conveying systems or automated warehousing environments.
Selecting the appropriate four-way directional valve tailored to your specific pneumatic actuator requirements enhances operational efficiency, reliability, and safety in your pneumatic control systems.
Related Reading


- Ellis/Kuhnke Controls
132 Lewis Street Unit A-2, Eatontown, N.J. 07724
Phone: 1-800-221-0714
Fax: 732-291-8154
Email: Info@ekci.com
- Home Pneumatic Controls Technical Info CAD Drawings Contact Us Pneumatic Timers Blog Site Map
