Significant Advancements: Overcoming Limitations in Pneumatic Actuators
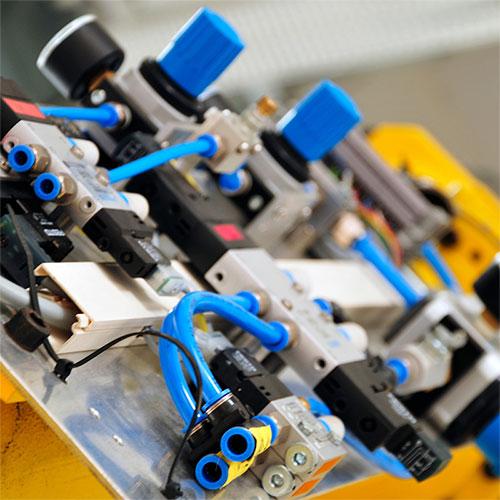 Pneumatic actuators, the backbone of industrial automation, have long been integral, providing essential force control for tasks like positioning, lifting, and actuating valves. However, they have historically faced limitations, mainly due to nonlinearity and poor damping, which affect their precision and reliability. The development of advanced control strategies has transformed these actuators, enabling them to overcome such challenges and expand their effectiveness across various industrial applications.
Pneumatic actuators, the backbone of industrial automation, have long been integral, providing essential force control for tasks like positioning, lifting, and actuating valves. However, they have historically faced limitations, mainly due to nonlinearity and poor damping, which affect their precision and reliability. The development of advanced control strategies has transformed these actuators, enabling them to overcome such challenges and expand their effectiveness across various industrial applications.
At the core of this evolution are pneumatic control systems that address the unique dynamic properties of pneumatic actuators. These control systems utilize advanced algorithms and techniques to compensate for the actuator response variability caused by air compressibility, load changes, and friction.
Tackling Nonlinearity and Damping with Modern Control Systems
One of the main issues with pneumatic actuators is nonlinearity, which stems from the compressibility of air and the variable behavior of actuators under different loads. When the air pressure changes within the actuator, the response can be unpredictable, leading to variations in speed and force. Traditionally, this would result in inconsistent performance, especially in systems that demand high precision.
Modern pneumatic control systems employ sophisticated strategies like sliding mode control and PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) control to overcome this. Sliding mode control is particularly effective because it allows the system to maintain stability even when the actuator's behavior changes due to load variations or shifts in air pressure. This control method continuously adjusts the actuator's response to match the desired output, minimizing any deviation from the intended path or movement. As a result, sliding mode control reduces overshoot—the tendency of the actuator to move beyond its target position, which can lead to inaccuracies or damage—leading to faster and more accurate operations in industries like robotics and manufacturing.
PID control, another widely used strategy, helps manage the relationship between air pressure, load, and actuator movement. By breaking down the control process into proportional, integral, and derivative actions, PID controllers can fine-tune the system's response to minimize errors. This technique is beneficial in reducing oscillations and ensuring the actuator reaches its target position smoothly without excessive vibrations. As a result, using PID control significantly improves damping performance, preventing instability that can slow down operations or cause damage to machinery.
The Role of Pneumatic Timers in Enhancing Actuator Performance
In addition to advanced control algorithms, pneumatic timers are essential to modern pneumatic control systems. These timers regulate compressed air flow to the actuators, ensuring that each movement happens in a precise, coordinated sequence. In industrial settings where timing is crucial—such as automated assembly lines (e.g., car manufacturing) or packaging systems (e.g., food packaging)—pneumatic timers help ensure that each task is executed precisely when needed, preventing overlaps or delays.
For instance, in an automated manufacturing process, pneumatic timers manage the intervals at which different actuators engage, ensuring that materials are moved, lifted, or assembled in perfect synchronization. This boosts productivity and prevents errors like misalignment or incomplete tasks, which can lead to costly downtime or product defects. By controlling the timing of airflow, these timers ensure that the actuators operate with maximum efficiency and precision, further optimizing the system's overall performance.
Getting the Most from Pneumatic Control Systems
Developing advanced control strategies for pneumatic actuators has significantly enhanced their capabilities, particularly in overcoming the traditional limitations of nonlinearity and poor damping. By integrating methods like sliding mode control and PID control and utilizing pneumatic timers for precise operation timing, industries have expanded the application of pneumatic actuators in environments that demand high precision and reliability. These advancements are pivotal in how pneumatic systems function, making them more adaptable, stable, and efficient in industrial automation.
Related Reading


- Ellis/Kuhnke Controls
132 Lewis Street Unit A-2, Eatontown, N.J. 07724
Phone: 1-800-221-0714
Fax: 732-291-8154
Email: Info@ekci.com
- Home Pneumatic Controls Technical Info CAD Drawings Contact Us Pneumatic Timers Blog Site Map
